Import a GitLab repository
This guide walks you through setting up Cube Cloud, importing a GitLab repository with an existing Cube project via SSH, and connecting to your database.
Step 1: Create an account
Navigate to cubecloud.dev , and create a new Cube Cloud account.
Step 2: Create a new Deployment
Click . This is the first step in the deployment creation. Give it a name and select the cloud provider and region of your choice.
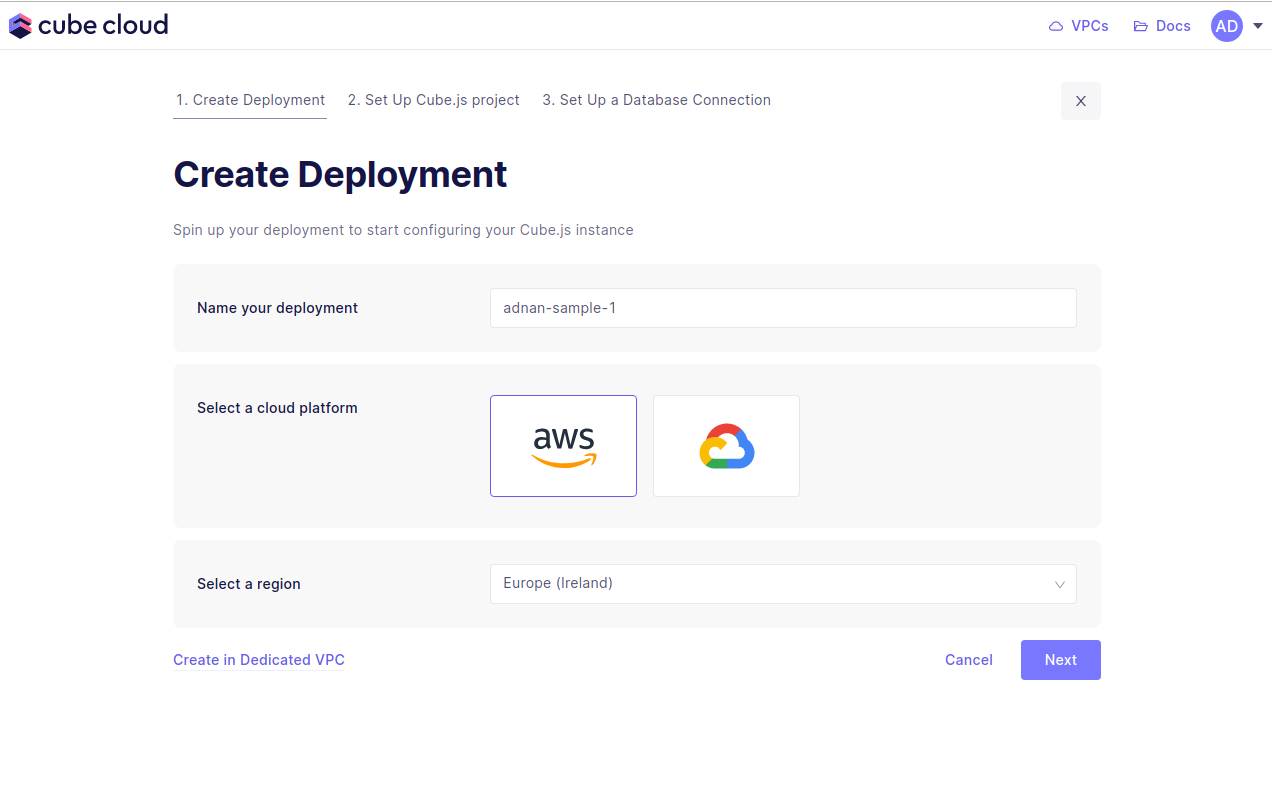
Microsoft Azure is available on Enterprise and above plans . Contact us for details.
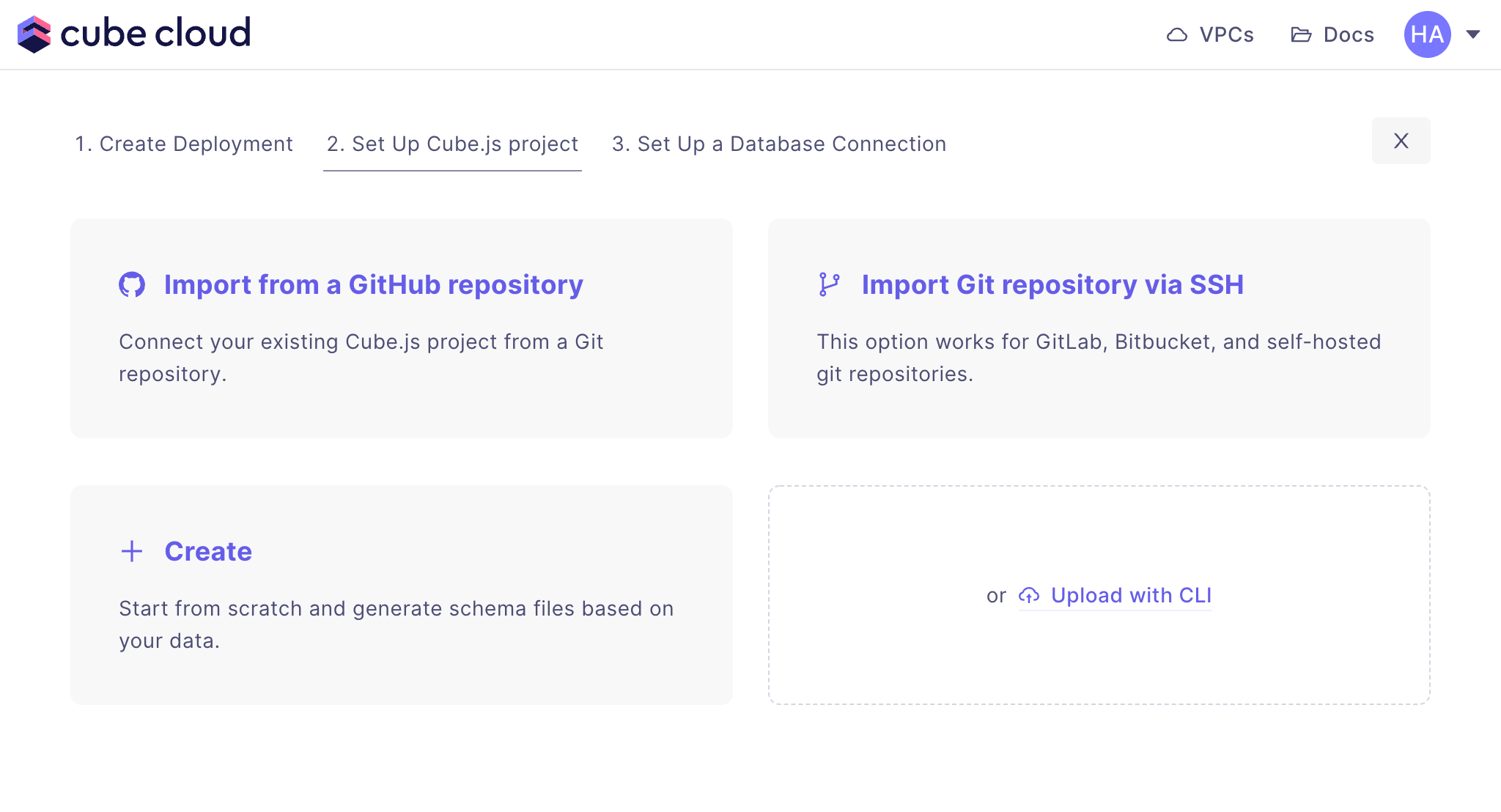
Step 3: Import Git repository
Next up, the second step in creating a Cube App from scratch in Cube Cloud is to click .
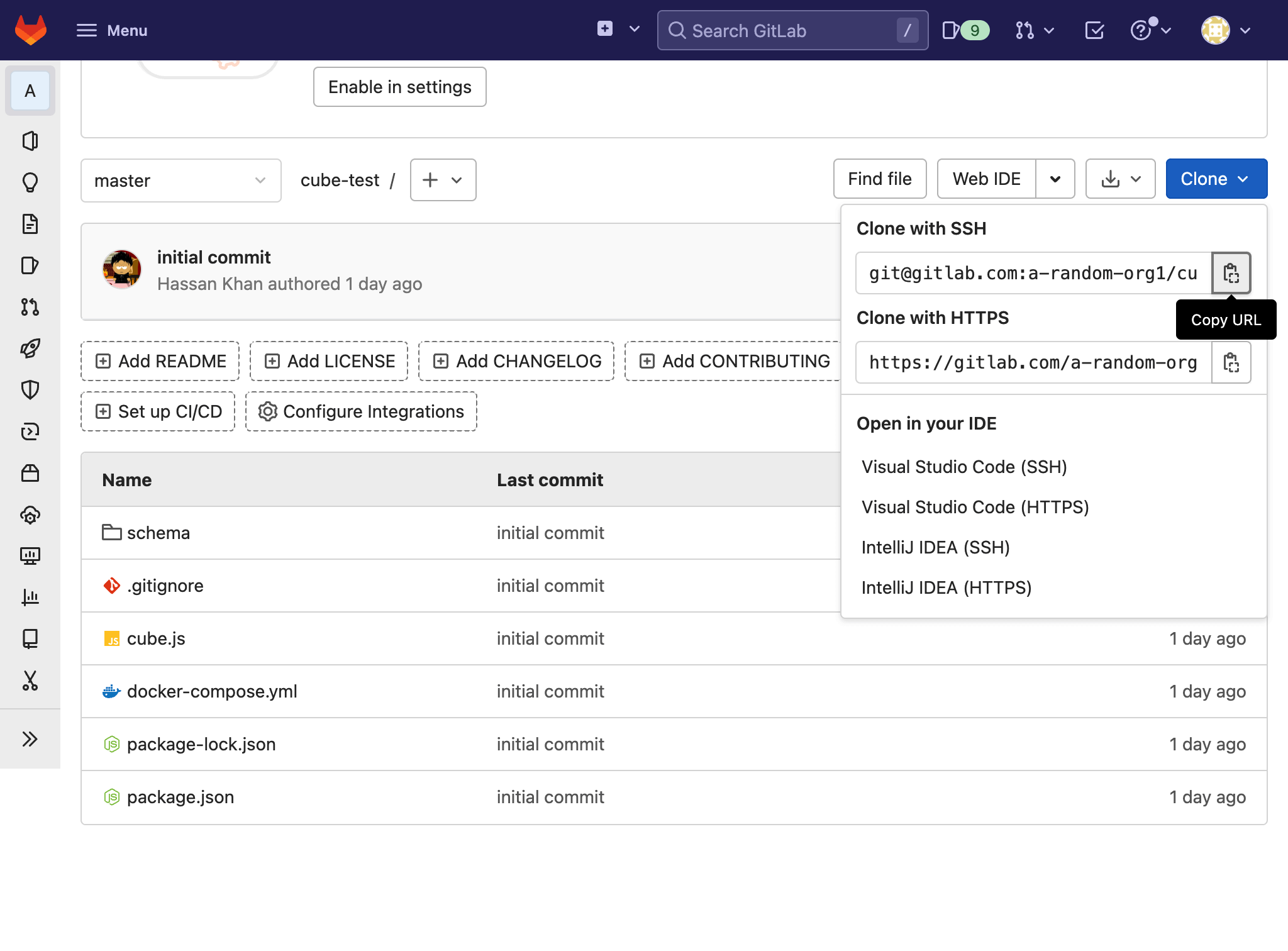
Now go to your GitLab repository and from the dropdown menu, copy the URL:
Back in Cube Cloud, paste the URL and click :
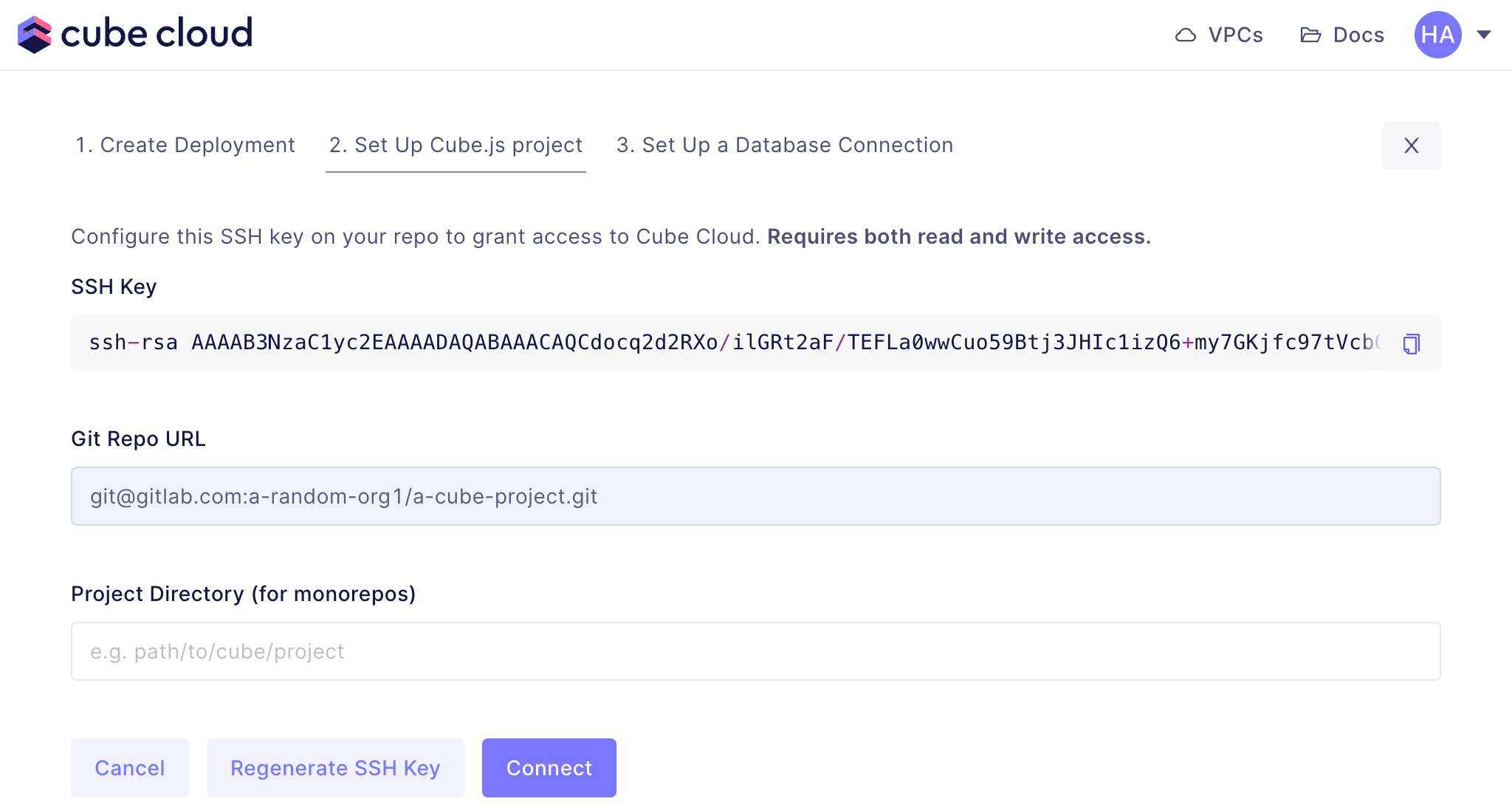
Now copy the SSH key and go back to GitLab and paste it into the repository’s
settings. Find the section and click .
Give the key a title (Cube Cloud, for example) and paste the SSH key in the
relevant field:
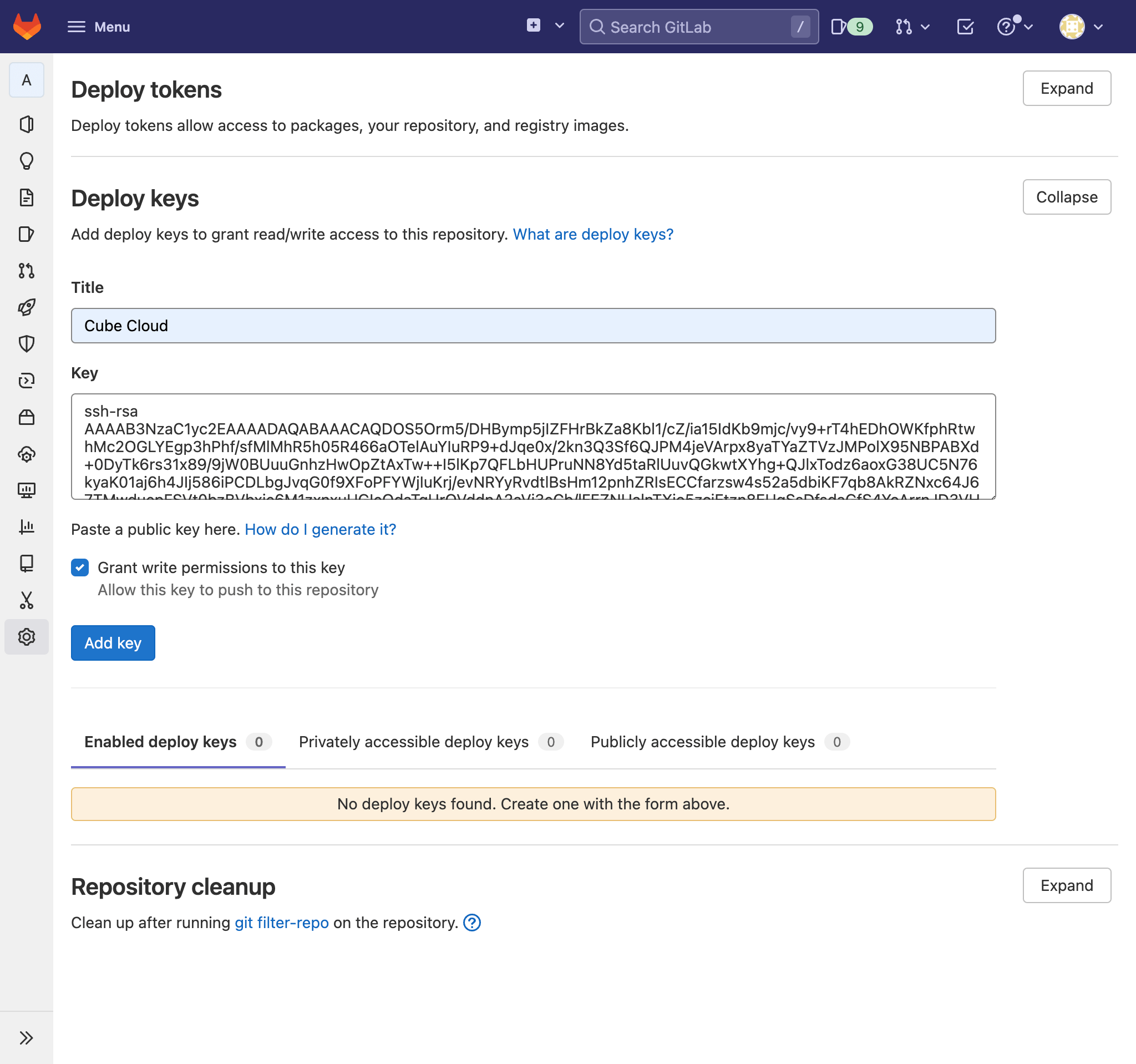
Ensure is checked, then click . Go back to Cube Cloud and click . After a connection is successfully established, you should see the next screen:
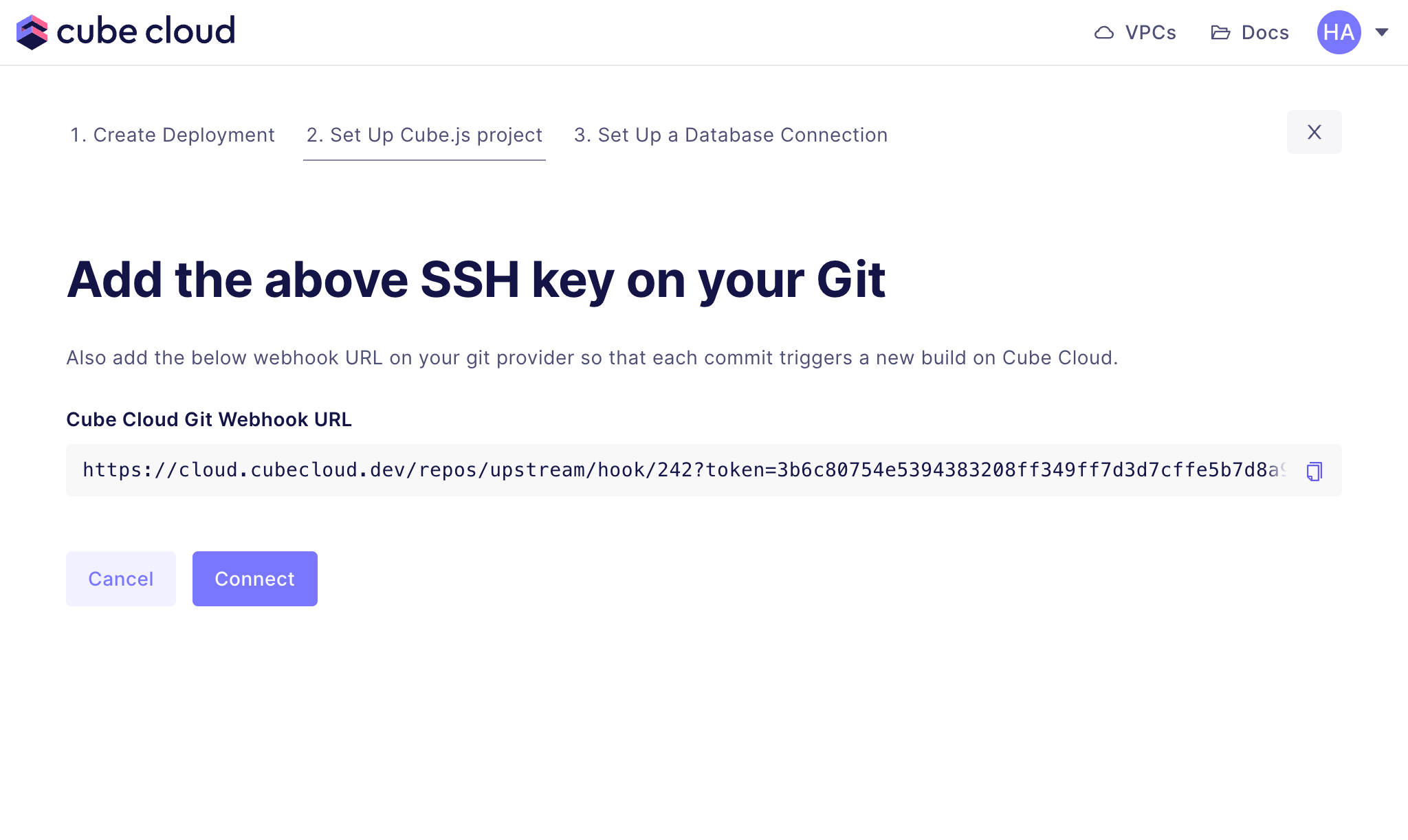
Copy the and go to your GitLab project’s settings. Paste the URL into the correct field, ensure the trigger is checked and click .
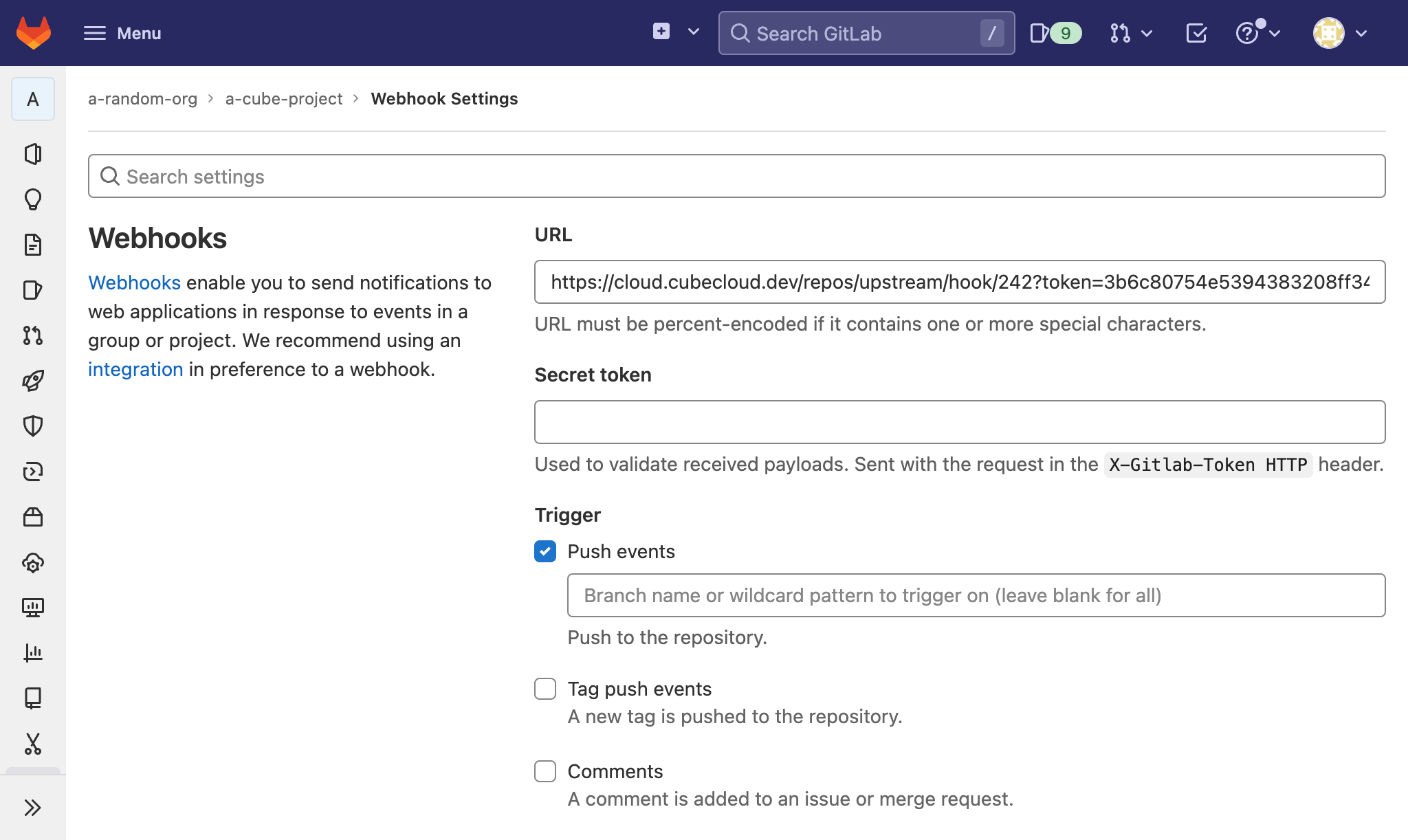
Back in Cube Cloud, click to test the webhook.
Step 4: Connect your Database
Enter your credentials to connect to your database. Check the connecting to databases guide for more details.
Want to use a sample database instead? We also have a sample database where you can try out Cube Cloud:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Host | demo-db.cube.dev |
| Port | 5432 |
| Database | ecom |
| Username | cube |
| Password | 12345 |
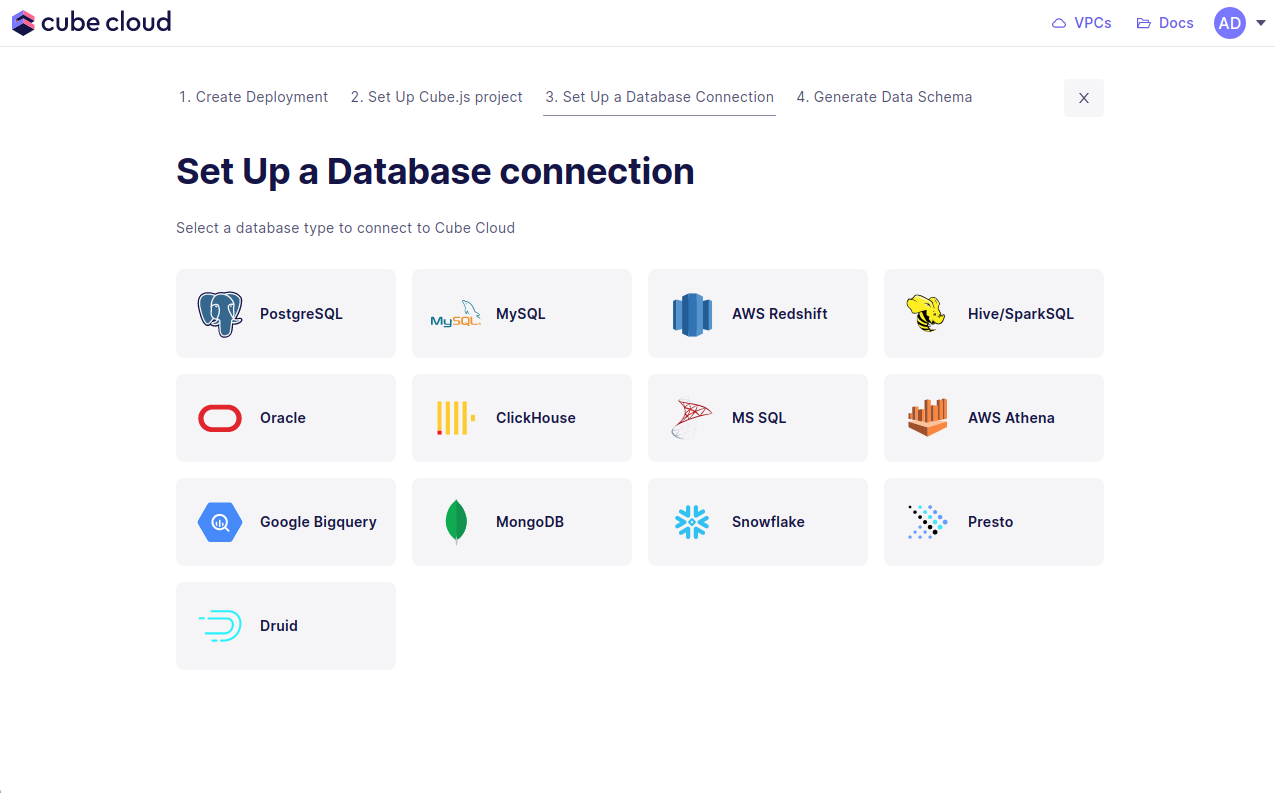
In the UI it’ll look exactly like the image below.
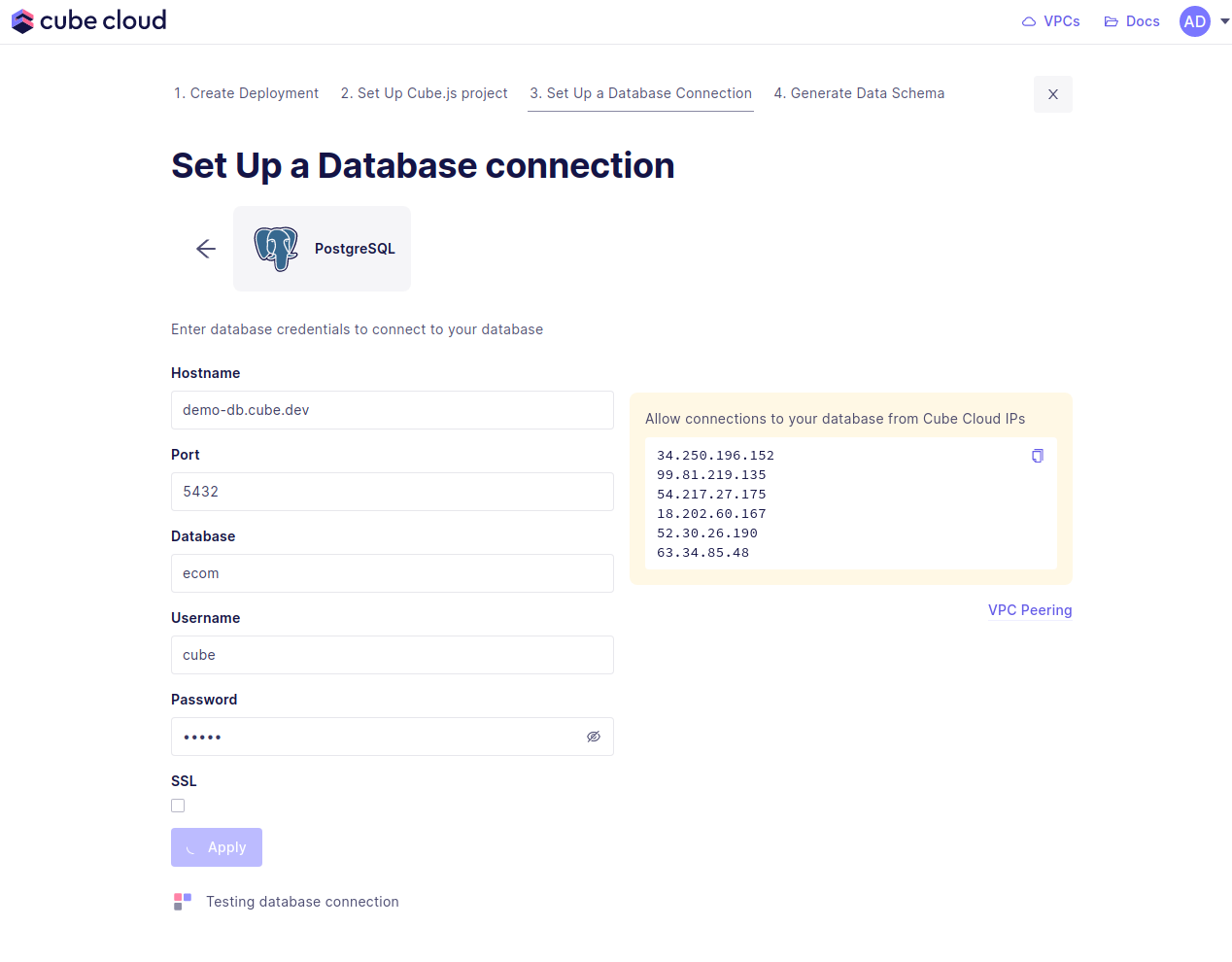
If you run into issues here, make sure to allow the Cube Cloud IPs to access your database. This means you need to enable these IPs in your firewall. If you are using AWS, this would mean adding a security group with allowed IPs.
Step 5: Generate the Data Model
Step five in this case consists of generating data models. Start by selecting the database tables to generate the data models from, then hit .
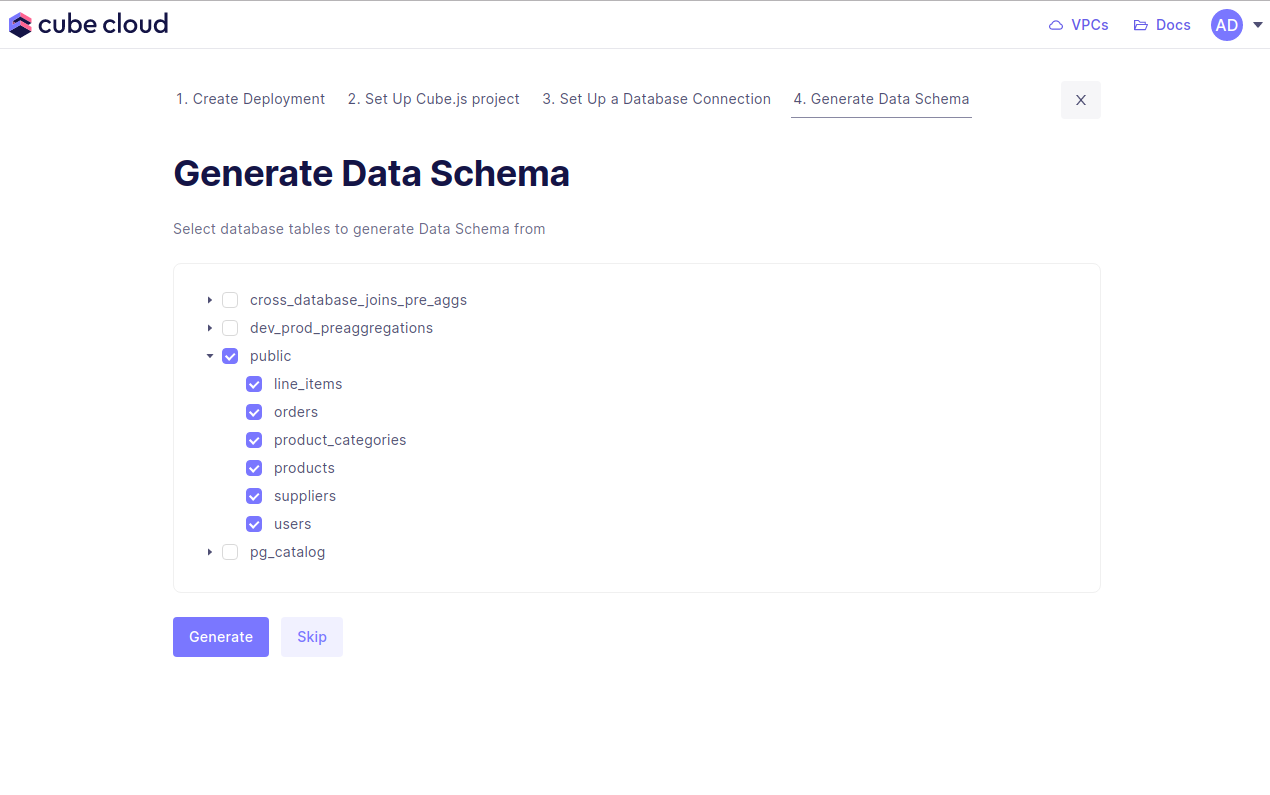
Cube Cloud will generate the data models and spin up your Cube deployment. With this, you’re done. You’ve created a Cube deployment, configured a database connection, and generated data models!
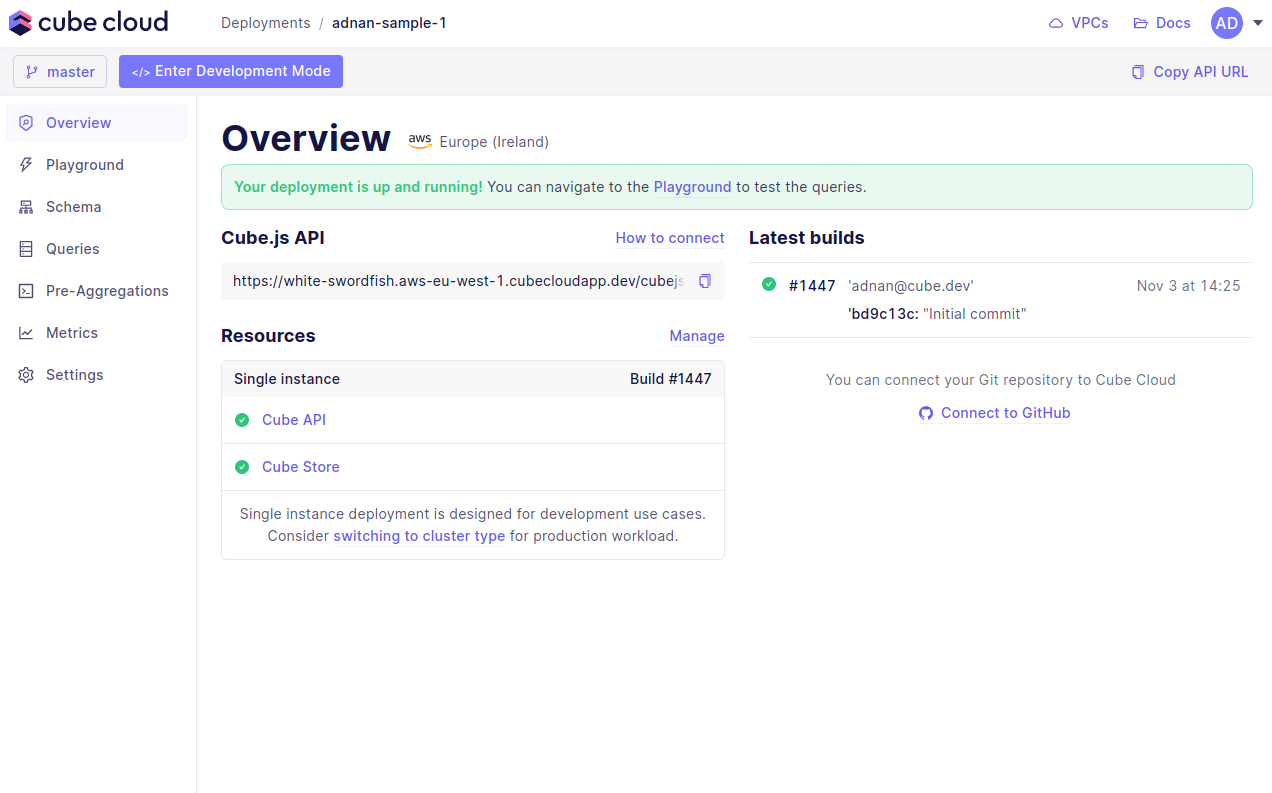
You’re ready for the last step, running queries in the Playground.
Step 6: Try out Cube Cloud
Now you can navigate to Playground to try out your queries or connect your application to the Cube Cloud API.
Was this page useful?